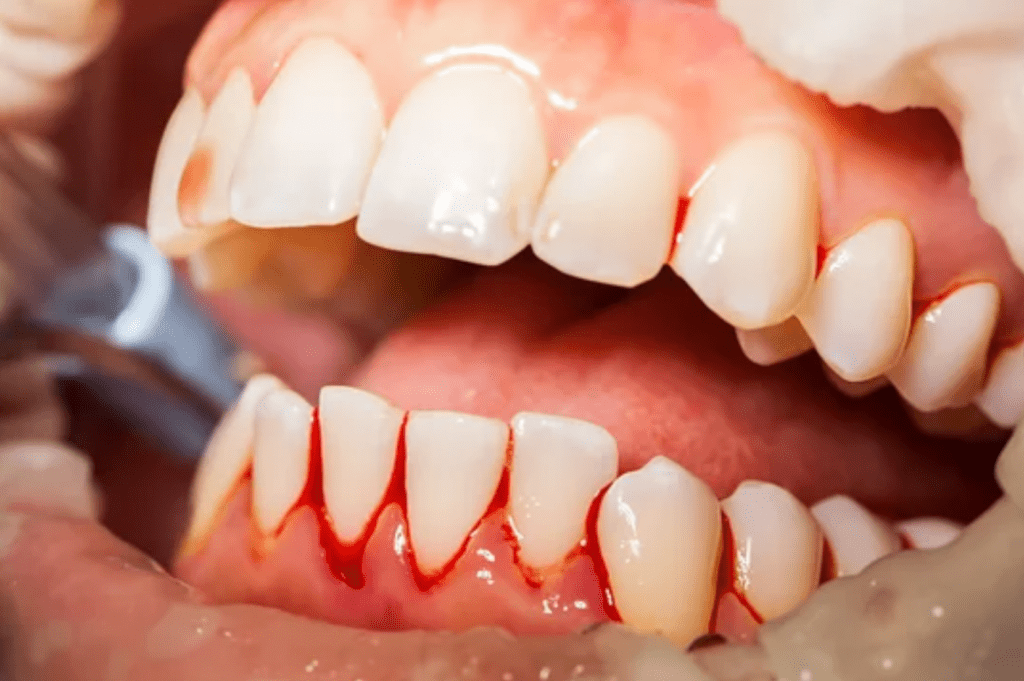
Gum disease is a severe oral health issue affecting millions worldwide. This disease can cause many symptoms, including bleeding gums, bad breath, and tooth loss. However, the effects of gum disease go beyond just oral health and can have huge implications for overall health and well-being.
Heart Disease
Recent research has shown a strong link between gum disease and heart disease. It is thought that the bacteria that cause gum disease can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation in the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis (hardening and narrowing of the arteries). Unfortunately, this can increase the risk of heart attack or stroke. In fact, people with gum disease are twice as likely to develop heart disease than those with healthy gums.
Diabetes
People with diabetes are at a higher risk for gum disease. In fact, research shows that the relationship between the two conditions goes hand-in-hand. Gum disease can make it harder to control blood sugar levels. Unfortunately, poorly controlled diabetes can cause gum disease to worsen. As a result, people with diabetes are three times more likely to develop gum disease than those without diabetes.
Respiratory Infections
Research has also shown a link between gum disease and respiratory infections, such as pneumonia. It is thought that the bacteria that cause gum disease can be inhaled into the lungs, where they can cause infections and other respiratory problems.
Pregnancy Complications
In addition, gum disease may lead to a higher risk of pregnancy complications, such as preterm birth and low birth weight. This is because the inflammation caused by gum disease can cause an immune response that may contribute to premature labor.
Dementia
Recent studies have also suggested a link between gum disease and cognitive decline. Researchers believe that the bacteria that cause gum disease can enter the brain and cause inflammation. This may contribute to the development of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia.
Prevention and Treatment
The good news is that gum disease is preventable and treatable with proper oral hygiene and professional dental care.
Brushing and flossing your teeth often can reduce the chances of gum disease. Most dentists recommend brushing at least twice a day and flossing daily. This will help remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and gums.
Additionally, visiting your dentist can lower your risks as well. When you visit the dentist, your dental team can examine and clean your teeth. This can help prevent and detect gum disease early on.
If you smoke or vape, you have a higher chance of developing gum disease. Smoking is a huge risk factor for gum disease and can make it harder to treat. Quitting these habits can lower your likelihood of gum disease and benefit your oral health.
If you develop gum disease, your dentist may recommend treatments, such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), antibiotics, or gum surgery to help control the infection and prevent further damage.
